Zamaporvint (RXC004, Porcupine Inhibitor)
Designed to unlock the potential of Wnt pathway blockade in oncology
Programme summary
Phase 2 programme combination data expected in H1 2024
Zamaporvint (RXC004), is a potent, selective, oral small molecule inhibitor of the enzyme, Porcupine, a key activator of Wnt-ligands in the Wnt signalling pathway.
Aberrant Wnt signalling contributes directly to tumour growth and plays an important role in immune resistance to treatment with immuno-oncology agents such as anti-PD-1 checkpoint inhibitors.
By selecting patients with tumours that have high Wnt-ligand dependency, such as tumours with mutations in the RNF43 gene and fusions in the RSPO gene family, zamaporvint has an opportunity to directly target the tumour in addition to having an immune-enhancing effect.
Our Phase 2 studies are in genetically-selected patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (monotherapy and immuno-oncology combination), genetically selected pancreatic cancer (monotherapy) and all-comers biliary cancer (monotherapy and immuno-oncology combination). These indications have significant unmet medical need, given poor survival outcomes and limited safe and effective treatment options.
Zamaporvint Clinical Development Overview
Our primary efficacy hypothesis for zamaporvint is in combination, which we are initially exploring clinically with anti-PD-1 therapy, where it has potential to overcome immune evasion and anti-PD-1 resistance in late-stage hard-to-treat tumour types. Additionally, due to its mechanism of action, there is further potential to combine with MAPK pathway inhibitors given the significant co-occurrence of both BRAF and KRAS mutations in Wnt-ligand dependent tumours, as well as with chemotherapy.
Zamaporvint Highlights to date
In Phase 1 study zamaporvint was found to:
- Be well tolerated active as a monotherapy, having differential clinical efficacy in Wnt-ligand dependent tumours (ESMO, 2021)
- Be well-tolerated in combination with nivolumab (SITC, 2022)
- Have pharmacokinetic profile suitable for once daily oral dosing.
- Showed target engagement (Axin-2 reduction) at all doses.
About the Phase 2 Programme:
The first trial, PORCUPINE, evaluates zamaporvint as a monotherapy and in combination with nivolumab (OPDIVO®1), an anti-PD-1 checkpoint immunotherapy in genetically selected MSS mCRC. The second trial, PORCUPINE2, evaluates zamaporvint as monotherapy in genetically selected pancreatic cancer and as monotherapy and in combination with pembrolizumab (KEYTRUDA®2), anti-PD-1 checkpoint immunotherapy in biliary tract cancer, given biliary tract cancer has high Wnt-ligand expression. In December 2022, a clinical trial collaboration and supply agreement with Merck was announced for the supply of pembrolizumab for this trial.
Phase 2 trial status:
- First data reported from biliary tract monotherapy module showed an active drug with modest monotherapy clinical benefit, supporting the use of zamaporvint in the combination setting
- Clinical trial collaboration and supply agreement in place with Merck for supply of pembrolizumab
- Patient recruitment for all modules is now closed
- We expect to report Phase 2 data during H1 2024
1 OPDIVO® is a registered trademark of Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
2 KEYTRUDA® is a registered trademark of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA
Phase 2 programme combination data expected in H1 2024
Zamaporvint (RXC004), is a potent, selective, oral small molecule inhibitor of the enzyme, Porcupine, a key activator of Wnt-ligands in the Wnt signalling pathway.
Aberrant Wnt signalling contributes directly to tumour growth and plays an important role in immune resistance to treatment with immuno-oncology agents such as anti-PD-1 checkpoint inhibitors.
By selecting patients with tumours that have high Wnt-ligand dependency, such as tumours with mutations in the RNF43 gene and fusions in the RSPO gene family, zamaporvint has an opportunity to directly target the tumour in addition to having an immune-enhancing effect.
Our Phase 2 studies are in genetically-selected patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (monotherapy and immuno-oncology combination), genetically selected pancreatic cancer (monotherapy) and all-comers biliary cancer (monotherapy and immuno-oncology combination). These indications have significant unmet medical need, given poor survival outcomes and limited safe and effective treatment options.
Zamaporvint Clinical Development Overview
Our primary efficacy hypothesis for zamaporvint is in combination, which we are initially exploring clinically with anti-PD-1 therapy, where it has potential to overcome immune evasion and anti-PD-1 resistance in late-stage hard-to-treat tumour types. Additionally, due to its mechanism of action, there is further potential to combine with MAPK pathway inhibitors given the significant co-occurrence of both BRAF and KRAS mutations in Wnt-ligand dependent tumours, as well as with chemotherapy.
Zamaporvint Highlights to date
In Phase 1 study zamaporvint was found to:
- Be well tolerated active as a monotherapy, having differential clinical efficacy in Wnt-ligand dependent tumours (ESMO, 2021)
- Be well-tolerated in combination with nivolumab (SITC, 2022)
- Have pharmacokinetic profile suitable for once daily oral dosing.
- Showed target engagement (Axin-2 reduction) at all doses.
About the Phase 2 Programme:
The first trial, PORCUPINE, evaluates zamaporvint as a monotherapy and in combination with nivolumab (OPDIVO®1), an anti-PD-1 checkpoint immunotherapy in genetically selected MSS mCRC. The second trial, PORCUPINE2, evaluates zamaporvint as monotherapy in genetically selected pancreatic cancer and as monotherapy and in combination with pembrolizumab (KEYTRUDA®2), anti-PD-1 checkpoint immunotherapy in biliary tract cancer, given biliary tract cancer has high Wnt-ligand expression. In December 2022, a clinical trial collaboration and supply agreement with Merck was announced for the supply of pembrolizumab for this trial.
Phase 2 trial status:
- First data reported from biliary tract monotherapy module showed an active drug with modest monotherapy clinical benefit, supporting the use of zamaporvint in the combination setting
- Clinical trial collaboration and supply agreement in place with Merck for supply of pembrolizumab
- Patient recruitment for all modules is now closed
- We expect to report Phase 2 data during H1 2024
1 OPDIVO® is a registered trademark of Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
2 KEYTRUDA® is a registered trademark of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA
Porcupine as an oncology target – why target Porcupine?
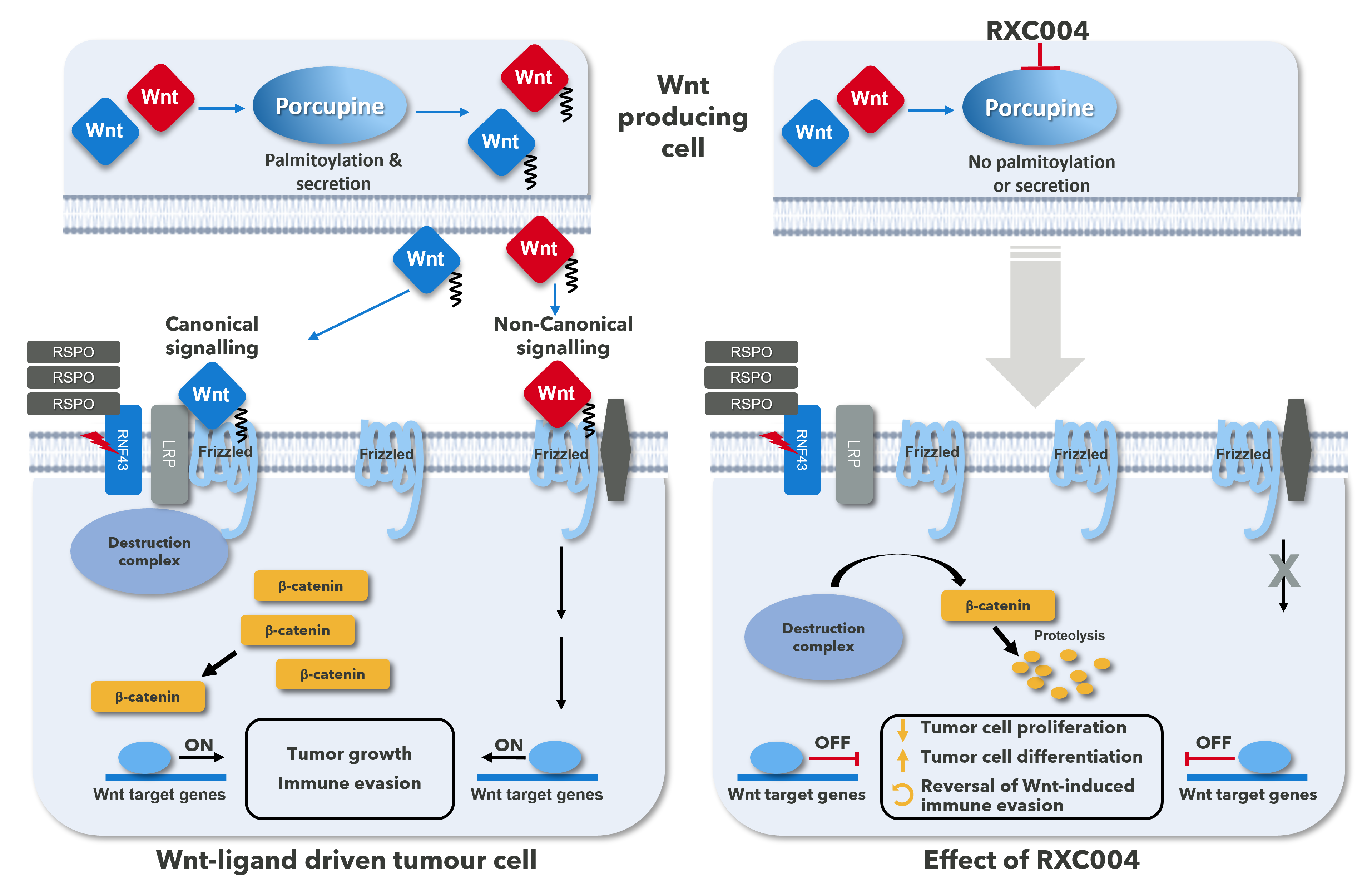
Signalling through the Wnt pathway is highly regulated at the level of ligand (Wnt), receptors (Fzd/LRP) and downstream components. The pathway is initiated by the binding of Wnt-ligands to Frizzled (Fzd) receptors resulting in activation of both the classical canonical and non-canonical signalling pathways.
Aberrant activation of the Wnt signalling pathway is involved in the initiation and progression of cancer. Activation of the Wnt pathway is also associated with poor prognosis and resistance of cancers to current therapies, including immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). The pathway is initiated by the binding of Wnt-ligands to Frizzled (Fzd) receptors resulting in activation of both the classical canonical and non-canonical signalling pathways (see Fig. 1). Porcupine is a key enzyme required for the release of all active Wnt-ligands and its inhibition will affect signalling via both canonical and non-canonical pathways, which are both involved in disease progression.
Clinical Development: RXC004 has a dual mechanism of action
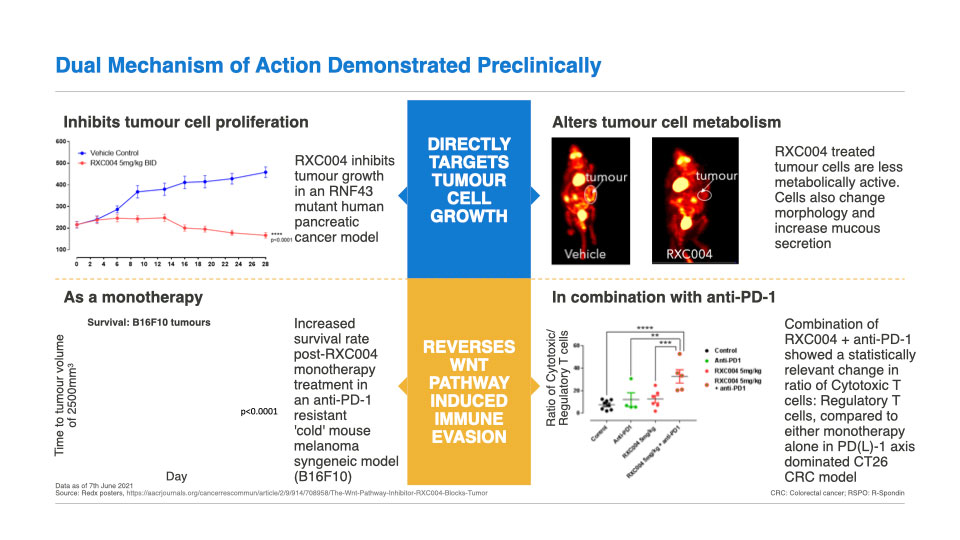
RXC004 has a dual mechanism of action, directly targeting tumour cells, in addition to having an immune-enhancing effect.
Preclinical in vitro and in vivo data have demonstrated that Porcupine inhibition has had significant anti-cancer effects in genetically defined cancer cells harbouring upstream Wnt pathway alterations such as RNF43 LoF mutations and RSPO-fusions. RNF43 LoF mutations and RSPO-fusions both result in increased levels of cell-surface Fzd receptors (see Fig. 1), and hence increased Wnt-ligand dependent signalling. Consistent with this, cancer cells carrying RNF43 LoF mutations and RSPO fusions/ translocations are particularly sensitive to Porcupine inhibition in vitro and in vivo.
In addition to targeting cancer cell growth directly, RXC004 has shown strong monotherapy efficacy in a mouse in vivo model that imitates a checkpoint inhibitor-resistant cancer patient. There is strong preclinical and clinical data linking Wnt pathway activation to immune evasion in cancer patients. Thus, in genetically defined cancer patients, RXC004 has potential to have a dual action; by directly inhibiting cancer cell growth and stimulating the patient’s immune system to help fight the cancer.
Source: Redx Published data – full detail in Posters (Phillips et al. 2019),(Woodcock et al. 2019).