Zelasudil (RXC007, ROCK2 inhibitor)
Next-generation selective ROCK2 inhibitor for the treatment of interstitial lung diseases with a Phase 2a trial underway in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Programme summary
Phase 2a clinical study commenced Q4 2022, topline data expected H1 2024
Zelasudil is a potent, highly selective and orally-active inhibitor that targets Rho-Associated Coiled-Coil Containing Protein Kinase 2 (ROCK2) which sits at a nodal point in cell signalling pathways, central to fibrosis. The role of ROCK2 in a diverse range of cellular processes allows zelasudil to have pleiotropic effects, affecting multiple cell signalling pathways associated with fibrosis. Selective inhibition of ROCK2 has the potential to prevent the hypotensive side effects typically associated with systemic pan-ROCK inhibitors (where both ROCK1 and ROCK2 are inhibited).
Our ROCK2 inhibitor, zelasudil, has demonstrated potential preclinically to be an attractive agent for the treatment of fibrotic indications. Additionally, zelasudil has shown preclinical proof-of-concept in immune-mediated models, which supports the development of zelasudil into other interstitial lung diseases beyond IPF, and in other fibrotic indications such as cancer-associated fibrosis.
Zelasudil Development Overview
ROCK2 signalling plays a key role in both the inflammatory component and the tissue remodelling that drives disease progression in many fibrotic conditions. Our approach was to apply our medicinal chemistry expertise to produce a next-generation ROCK2 inhibitor with optimised characteristics including selectivity to improve safety profile and side effects, reduce drug-drug interaction liabilities and to have improved physicochemical properties to achieve increased exposures at lower doses.
The orphan disease idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a severe and life-threatening chronic lung condition is being targeted as the first indication for clinical development. With a very poor prognosis, similar to many cancers, and limited treatment options, IPF affects over 170,000 patients in the US, EU5 and Japan alone. Zelasudil is currently in a Phase 2 trial for IPF but has also shown promising outcomes in a number of preclinical models for other interstitial lung diseases and cancer-associated fibrosis.
Zelasudil has been shown to be safe and well tolerated in a Phase 1 clinical study in healthy volunteers and is now being progressed in a Phase 2a clinical study in patients with IPF.
Zelasudil Highlights to date
In Phase 1 study in healthy volunteers:
- Zelasudil confirms good safety and pharmacokinetic profile
- Safe and well tolerated with few treatment emergent adverse events reported
- No evidence of hypotension validating rationale for selective ROCK2 inhibition
- Mean half-life of 9-11 hours potentially suitable for once or twice daily dosing.
Preclinical studies:
Zelasudil activity as well as in patient tissue in both chemically induced and immune-mediated preclinical models supports the core development plan in IPF and other interstitial lung diseases. Zelasudil was seen to be efficacious in several in vivo preclinical models of fibrosis, including:
- Therapeutic Murine Bleomycin-induced IPF Model
- Therapeutic Murine Sclerodermatous chronic Graft versus Host (immune mediated ILD) mode
- Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver fibrosis model
- Human fibrotic lung tissue isolated from resected lung.
Additionally, zelasudil has shown promising results in Therapeutic Murine Pancreatic Cancer Patient Derived Xenograft model, supporting a development plan in cancer-associated fibrosis.
Phase 2a clinical study commenced Q4 2022, topline data expected H1 2024
Zelasudil is a potent, highly selective and orally-active inhibitor that targets Rho-Associated Coiled-Coil Containing Protein Kinase 2 (ROCK2) which sits at a nodal point in cell signalling pathways, central to fibrosis. The role of ROCK2 in a diverse range of cellular processes allows zelasudil to have pleiotropic effects, affecting multiple cell signalling pathways associated with fibrosis. Selective inhibition of ROCK2 has the potential to prevent the hypotensive side effects typically associated with systemic pan-ROCK inhibitors (where both ROCK1 and ROCK2 are inhibited).
Our ROCK2 inhibitor, zelasudil, has demonstrated potential preclinically to be an attractive agent for the treatment of fibrotic indications. Additionally, zelasudil has shown preclinical proof-of-concept in immune-mediated models, which supports the development of zelasudil into other interstitial lung diseases beyond IPF, and in other fibrotic indications such as cancer-associated fibrosis.
Zelasudil Development Overview
ROCK2 signalling plays a key role in both the inflammatory component and the tissue remodelling that drives disease progression in many fibrotic conditions. Our approach was to apply our medicinal chemistry expertise to produce a next-generation ROCK2 inhibitor with optimised characteristics including selectivity to improve safety profile and side effects, reduce drug-drug interaction liabilities and to have improved physicochemical properties to achieve increased exposures at lower doses.
The orphan disease idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a severe and life-threatening chronic lung condition is being targeted as the first indication for clinical development. With a very poor prognosis, similar to many cancers, and limited treatment options, IPF affects over 170,000 patients in the US, EU5 and Japan alone. Zelasudil is currently in a Phase 2 trial for IPF but has also shown promising outcomes in a number of preclinical models for other interstitial lung diseases and cancer-associated fibrosis.
Zelasudil has been shown to be safe and well tolerated in a Phase 1 clinical study in healthy volunteers and is now being progressed in a Phase 2a clinical study in patients with IPF.
Zelasudil Highlights to date
In Phase 1 study in healthy volunteers:
- Zelasudil confirms good safety and pharmacokinetic profile
- Safe and well tolerated with few treatment emergent adverse events reported
- No evidence of hypotension validating rationale for selective ROCK2 inhibition
- Mean half-life of 9-11 hours potentially suitable for once or twice daily dosing.
Preclinical studies:
Zelasudil activity as well as in patient tissue in both chemically induced and immune-mediated preclinical models supports the core development plan in IPF and other interstitial lung diseases. Zelasudil was seen to be efficacious in several in vivo preclinical models of fibrosis, including:
- Therapeutic Murine Bleomycin-induced IPF Model
- Therapeutic Murine Sclerodermatous chronic Graft versus Host (immune mediated ILD) mode
- Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver fibrosis model
- Human fibrotic lung tissue isolated from resected lung.
Additionally, zelasudil has shown promising results in Therapeutic Murine Pancreatic Cancer Patient Derived Xenograft model, supporting a development plan in cancer-associated fibrosis.
Zelasudil is a next generation ROCK2 selective inhibitor with potential to improve safety and therapeutic outcomes
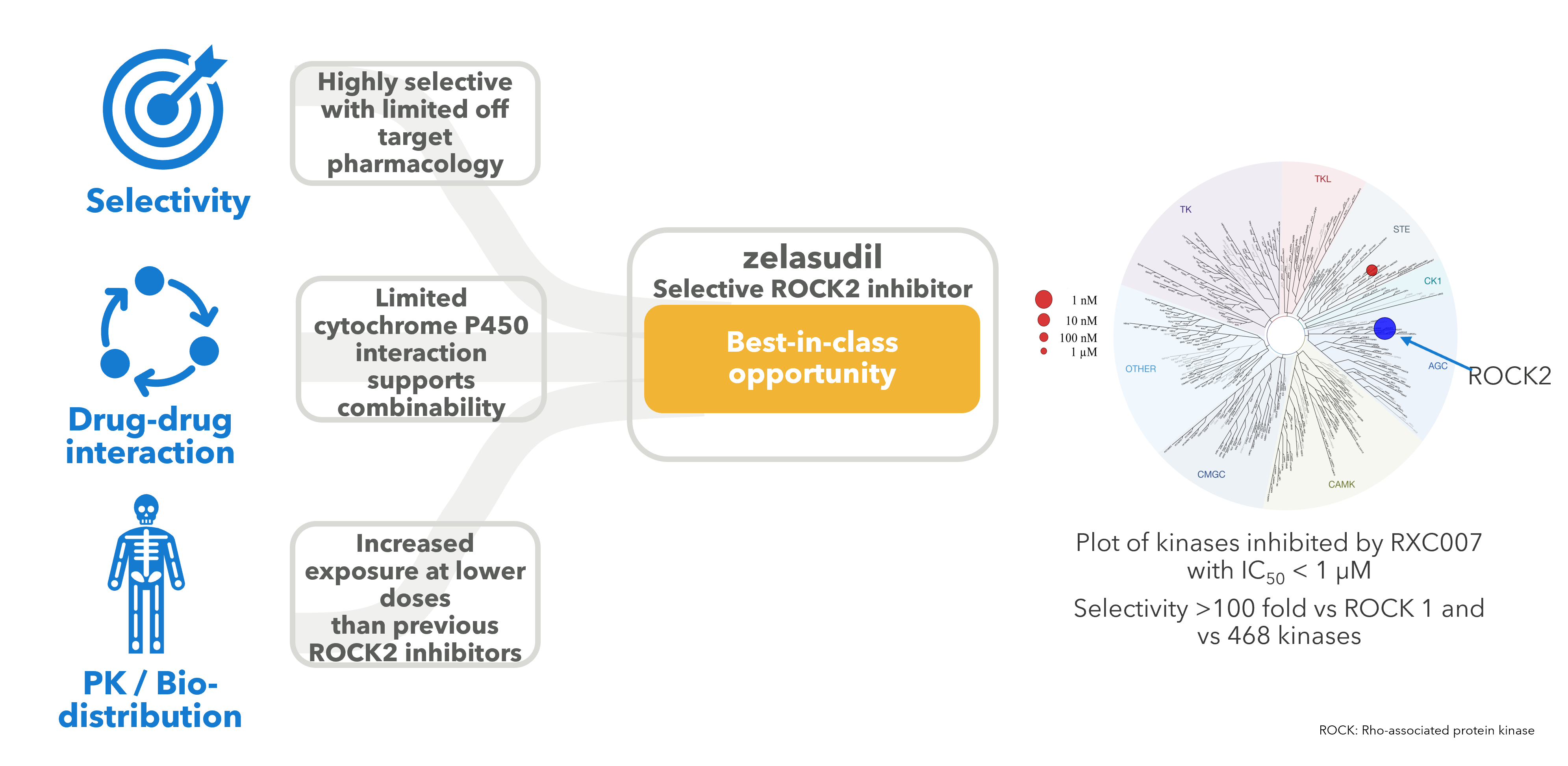
Our approach in the ROCK2 project was to apply our medicinal chemistry expertise to produce a next generation ROCK2 inhibitor with improved characteristics including improved selectivity to improve safety and side effects, to have lower cytochrome P450 actions to reduce drug-drug interaction liabilities and to have improved physicochemical properties to achieve increased exposures at lower doses.
ROCK2 is an intracellular kinase with multiple cellular functions. ROCK2 sits at a nodal point in a cell signalling pathway, believed to be central to fibrosis
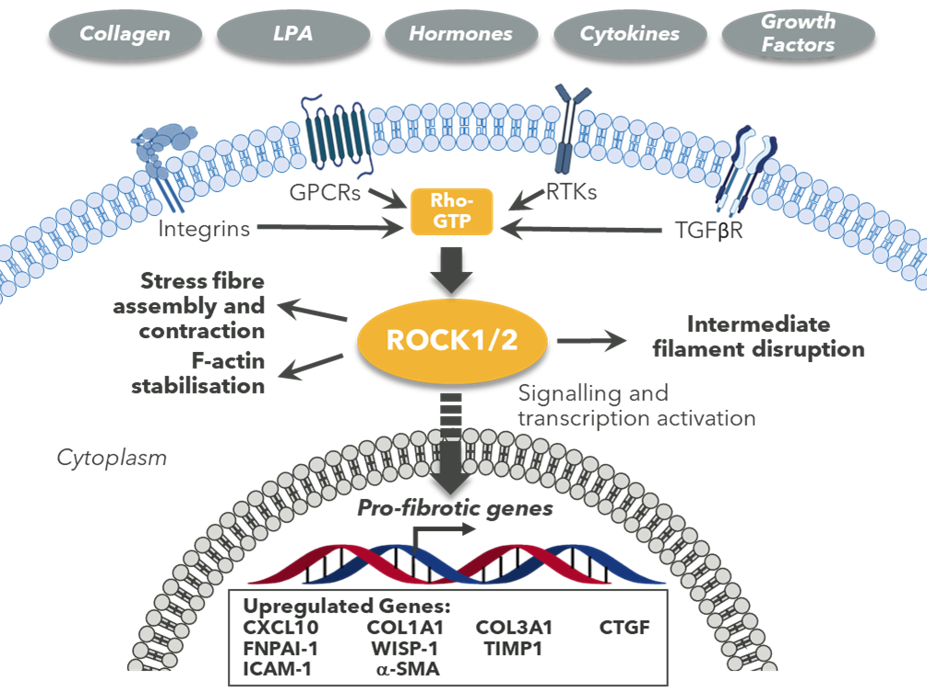
ROCK2 signalling plays a key role in both the inflammatory component and the tissue remodelling that drives disease progression in many fibrotic conditions. ROCK2 expression and activity have been shown to be upregulated in acute inflammatory injury and in chronic diseases such as diabetes, metabolic syndrome and IPF. Selective inhibition of ROCK2 has the potential to prevent the hypotensive side effects typically associated with systemic pan-ROCK inhibitors (where both ROCK1 and ROCK2 are inhibited).
Zelasudil Activity on Patient Tissue and in Preclinical Models Supports Core Development Plan in IPF and CF-ILDs
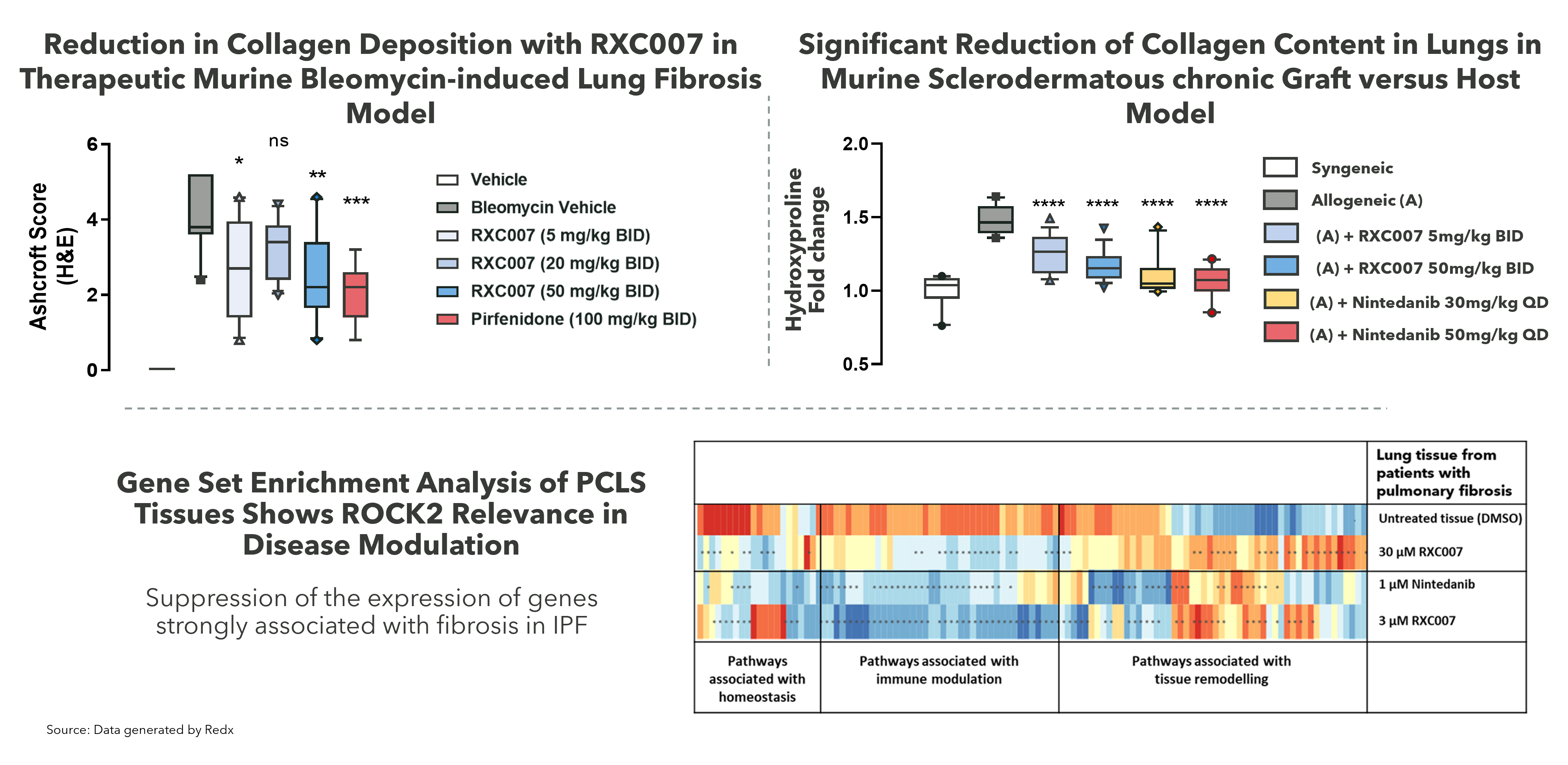
Zelasudil has a strong preclinical package in lung fibrosis which underpins our approach in the clinic. It has shown good anti-fibrotic effects in both immune mediated and chemically induced models of lung fibrosis as is shown in the top 2 graphs, where there is strong inhibition of collagen deposition in the lung. In the bottom panel there is strong modulation of key fibrosis genes in human diseased tissue derived from lung fibrosis patients who have undergone transplant therapy.
Phase 1 data in healthy volunteers confirms good safety and pharmacokinetic profile
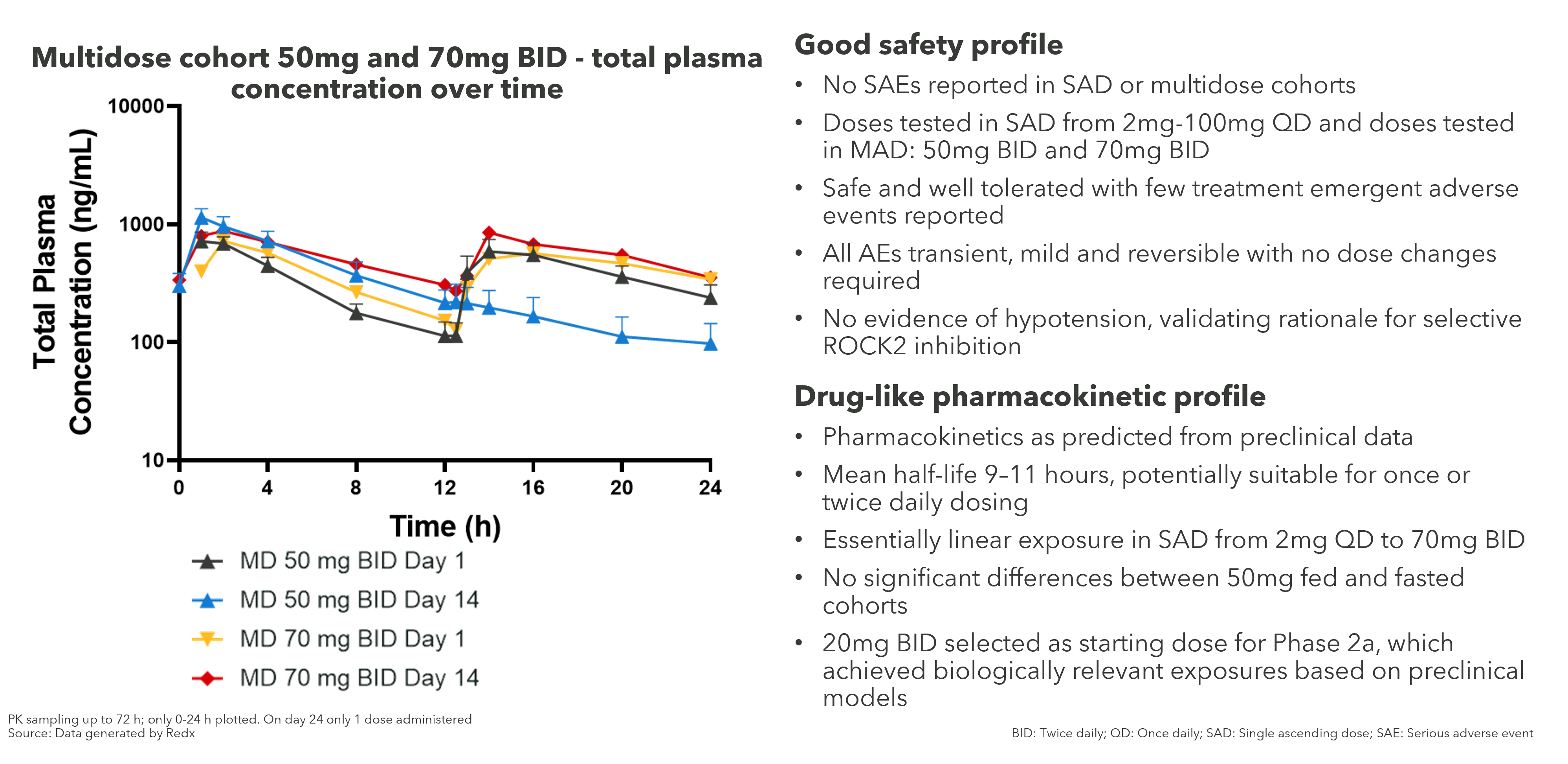
The zelasudil Phase 1 trial in health volunteers show the overall pharmacokinetic profile to be as predicted from the preclinical data and the plasma concentration increases have been essentially linear, showing a drug-like pharmacokinetic profile.
Phase 2a Study in IPF Patients Ongoing with Data Readout Expected H1 2024
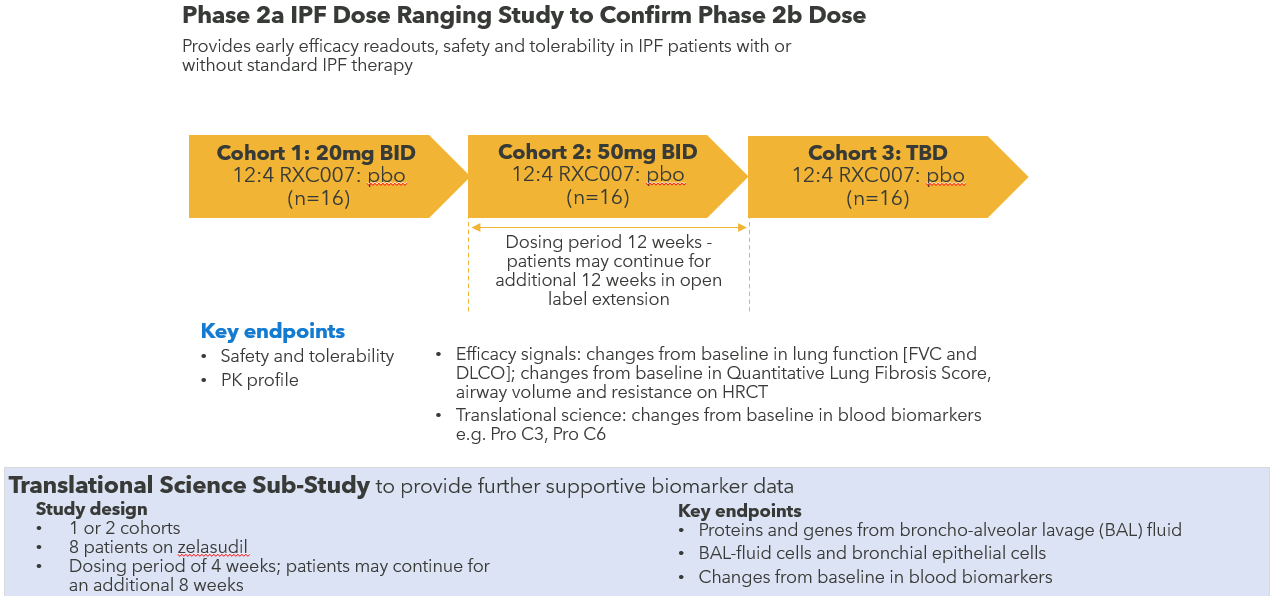
Phase 2a dose ranging study to provide early efficacy readouts, safety and tolerability in IPF patients with or without standard IPF therapy. The dosing duration of the main study is 12 weeks and although the study primarily provides safety and pharmacokinetic data, there will also be early readouts on FVC and other efficacy endpoints. Additionally, a 28-day translational science sub-study will provide more detailed data on biomarkers from lung samples taken at pre and post treatment bronchoscopies.