RXC008 (GI-targeted pan-ROCK inhibitor)
Potential first-in-class treatment for fibrostenotic Crohn’s disease
Programme summary
Phase 1 clinical study commenced Q1 2024, healthy volunteer data expected H2 2024
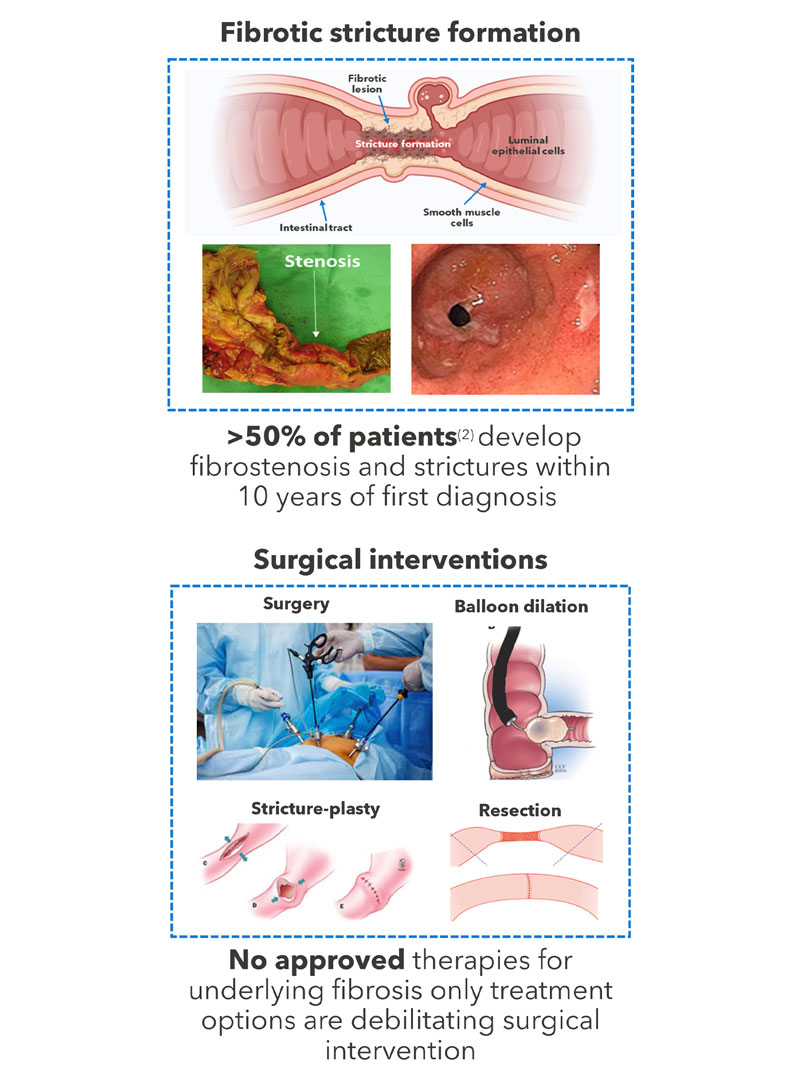
Crohn’s disease affects 1.7m* people globally and >70,000 new cases are diagnosed each year. More than 50% of patients** with Crohn’s disease can develop significant fibrosis and stricture formation within ten years after diagnosis; this fibrosis associated with Crohn’s disease is known as fibrostenotic Crohn’s disease.
The current management of fibrotic strictures of the gastrointestinal tract is primarily surgical as no drugs are specifically approved for fibrosis, which can progress despite intervention with anti-inflammatory therapies.
Relapse rate post-surgical intervention is high with >50% patients requiring further surgery within 10 years, many within 12 months. Consequently, patients suffer progressive loss of gastrointestinal function and repeated resections can lead to major health complications such as short bowel syndrome.
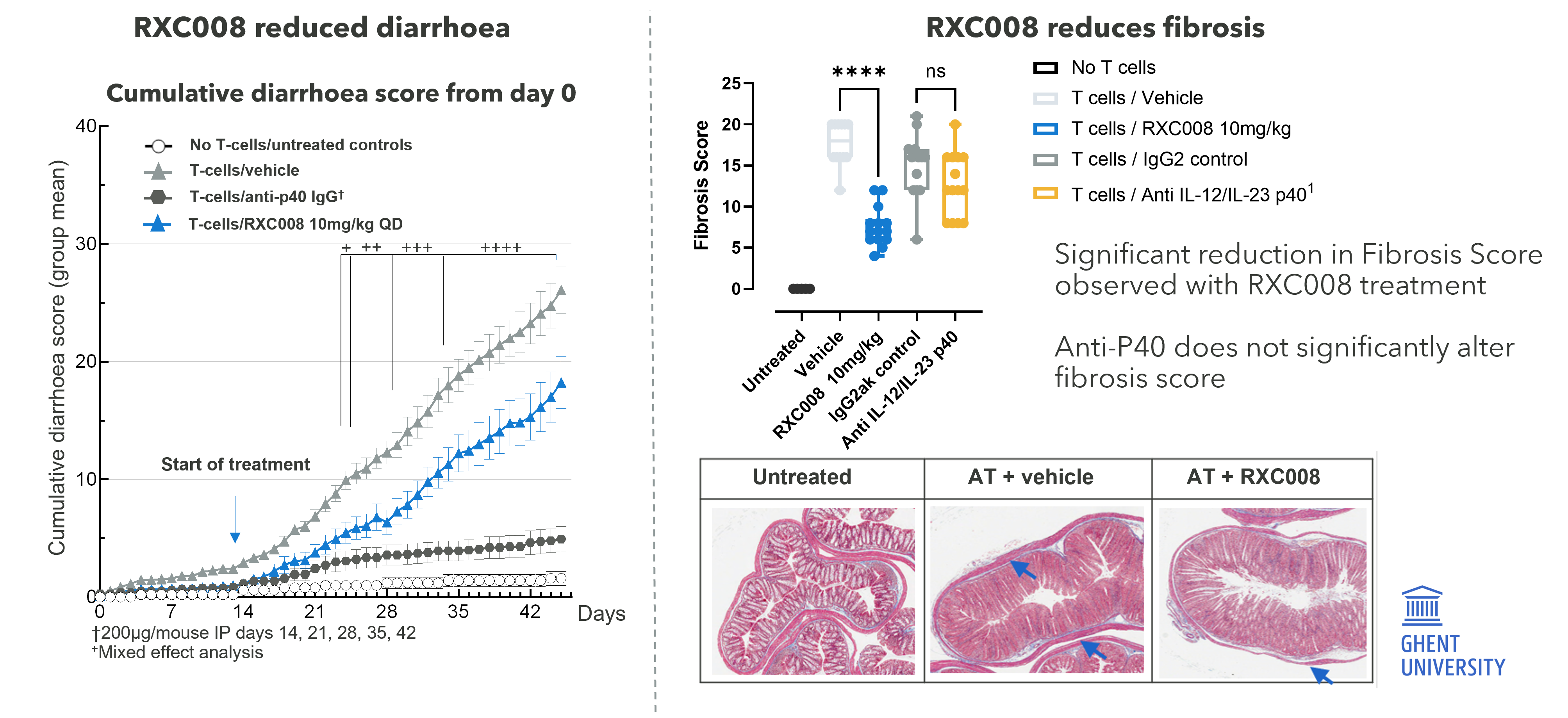
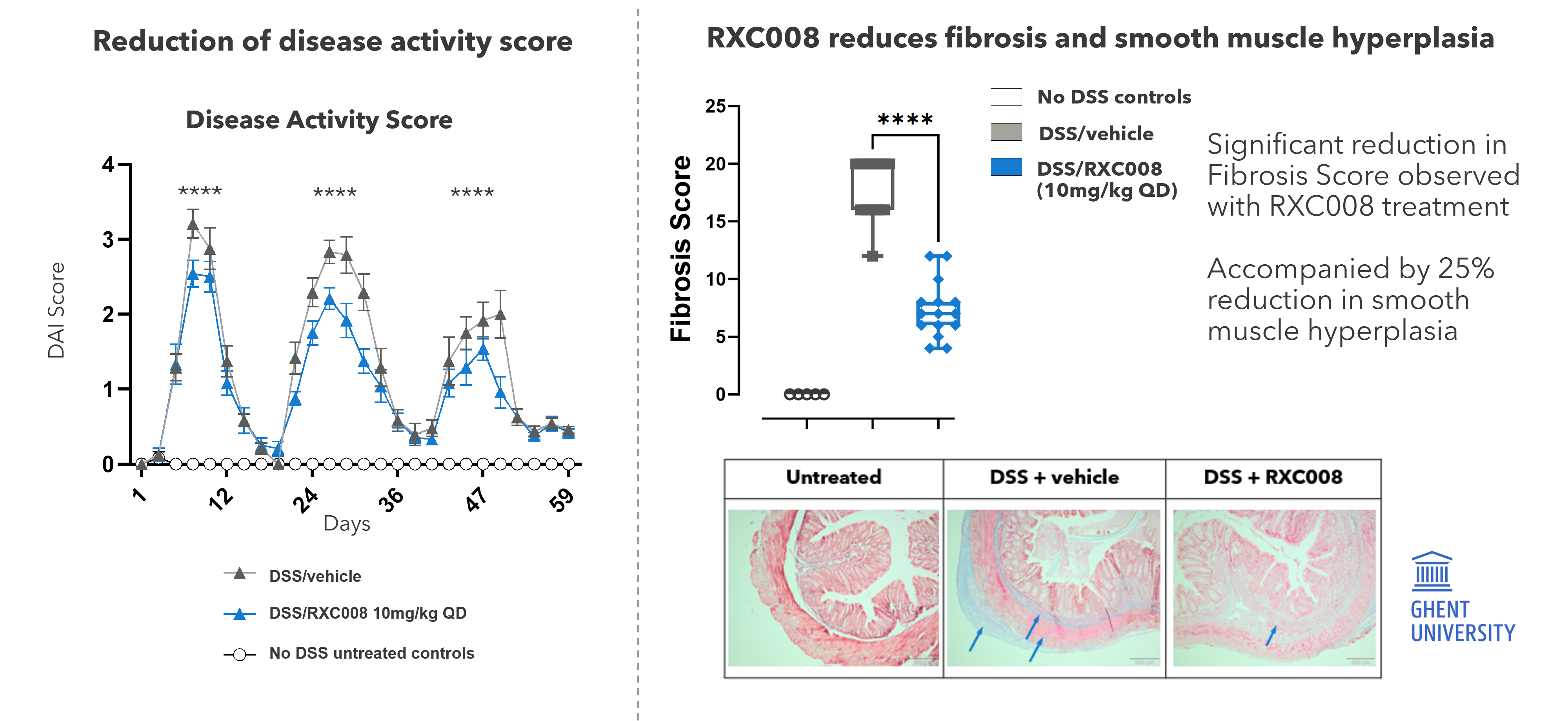
RXC008 is designed to work specifically at the site of fibrosis in the gastrointestinal tract and to degrade quickly, if absorbed into the bloodstream, through enzyme-mediated metabolism. Preclinical data from our GI-targeted pan-ROCK inhibitor research project shows strong anti-fibrotic therapeutic effects in multiple animal models of inflammatory bowel disease.
We commenced a Phase 1 clinical study in Q1 2024 and expect to report healthy volunteer data by the end of 2024.
Refs: * Clarivate, Crohn’s disease landscape & forecast pg 39, Published Sep 2022; ** Chan et al, 2018
Phase 1 clinical study commenced Q1 2024, healthy volunteer data expected H2 2024
Crohn’s disease affects 1.7m* people globally and >70,000 new cases are diagnosed each year. More than 50% of patients** with Crohn’s disease can develop significant fibrosis and stricture formation within ten years after diagnosis; this fibrosis associated with Crohn’s disease is known as fibrostenotic Crohn’s disease.
The current management of fibrotic strictures of the gastrointestinal tract is primarily surgical as no drugs are specifically approved for fibrosis, which can progress despite intervention with anti-inflammatory therapies.
Relapse rate post-surgical intervention is high with >50% patients requiring further surgery within 10 years, many within 12 months. Consequently, patients suffer progressive loss of gastrointestinal function and repeated resections can lead to major health complications such as short bowel syndrome.
RXC008 is designed to work specifically at the site of fibrosis in the gastrointestinal tract and to degrade quickly, if absorbed into the bloodstream, through enzyme-mediated metabolism. Preclinical data from our GI-targeted pan-ROCK inhibitor research project shows strong anti-fibrotic therapeutic effects in multiple animal models of inflammatory bowel disease.
We commenced a Phase 1 clinical study in Q1 2024 and expect to report healthy volunteer data by the end of 2024.
Refs: * Clarivate, Crohn’s disease landscape & forecast pg 39, Published Sep 2022; ** Chan et al, 2018
ROCK is a nodal point for pro-fibrotic signalling in Fibrostenosis
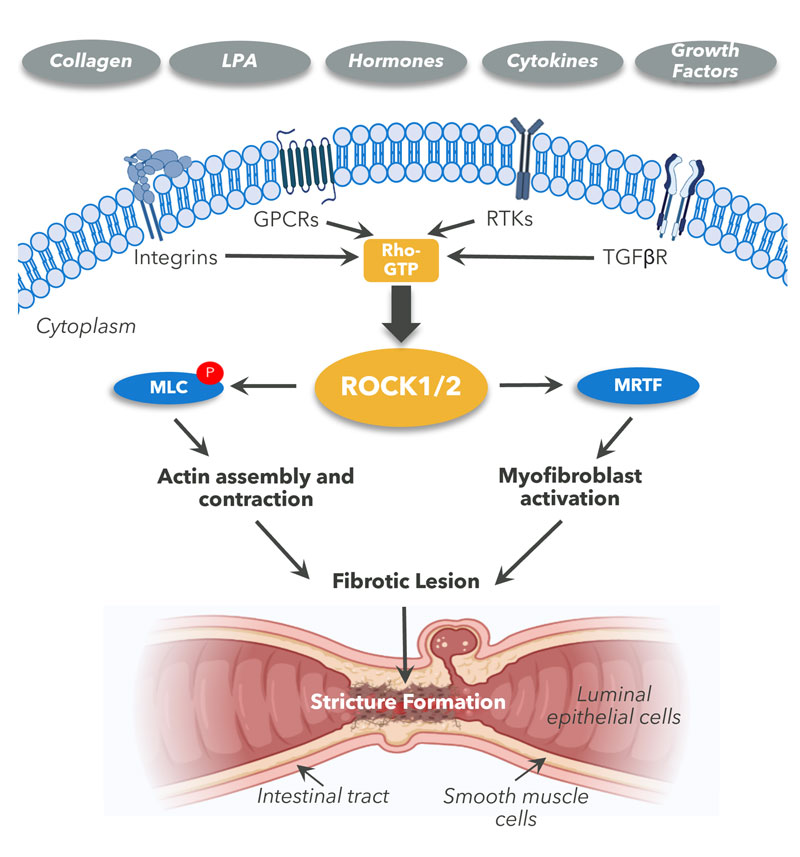
Fibrostenosis in Crohn’s Disease is caused by excessive build-up of collagen and fibrotic extra-cellular matrix leading to narrowing of the GI tract and obstruction. There is no current pharmaceutical treatment. ROCK signalling is involved in controlling several fibrotic responses such as fibroblast activation and migration, epithelial cell apoptosis, epithelial tight junction assembly and EMT (Epithelial to mesenchymal transition).